Bodenstein Number

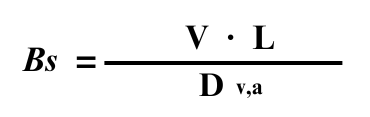
The Bodenstein number (Bo) is a dimensionless parameter used in chemical engineering and fluid dynamics to characterize the relative importance of chemical reaction rates to mass transfer rates in a reacting flow system. It’s named after Max Ernst August Bodenstein, a German physical chemist known for his contributions to the study of chemical kinetics.
Bodenstein number is used in mass transfer in general and diffusion in reactors calculations in particular.
It is normally defined in the following form :
Where: | ||
Dv,a | = | Effective axial diffusivity |
L | = | Reactor length |
V | = | Velocity |
The Bodenstein number helps determine whether chemical reactions or mass transfer processes dominate the behavior of the system. Depending on the value of the Bodenstein number, different regimes of reaction and mass transfer can be identified:
- If Bo ≪ 1, mass transfer dominates over chemical reaction, and the overall behavior is primarily controlled by the rate of mass transfer. This typically occurs when the characteristic reaction time is much longer than the characteristic mass transfer time.
- If Bo ≫ 1, chemical reaction dominates over mass transfer, and the overall behavior is primarily controlled by the rate of chemical reaction. This typically occurs when the characteristic reaction time is much shorter than the characteristic mass transfer time.
The Bodenstein number is commonly used in the analysis and design of chemical reactors, combustion systems, and other reacting flow systems. It helps engineers and scientists understand and predict the behavior of chemical reactions in the presence of mass transfer limitations.

