Elasticity Number

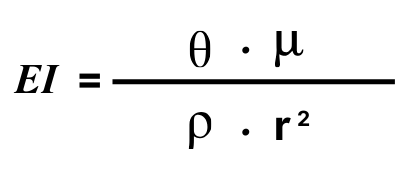
In the context of fluid mechanics and pipe flow, the term “elasticity number” typically refers to a dimensionless parameter used to characterize the behavior of a fluid flowing through a pipe.
The elasticity number represents the ratio of the elastic forces to the viscous forces within the fluid flow. It’s defined differently depending on the specific application, but one common formulation for the elasticity number in pipe flow above
Where: | ||
r | = | Pipe/conduit radius |
mu | = | Viscosity |
rho | = | Density |
theta | = | relaxation time |
- Elastic forces typically arise due to the deformation of the fluid or the pipe wall.
- Viscous forces arise due to the fluid’s viscosity and are related to the rate of deformation.
Understanding the elasticity number helps in predicting the behavior of viscoelastic fluids (such as certain types of polymer solutions) in pipe flow, where both elastic and viscous effects are significant. Depending on the value of the elasticity number, the flow can exhibit different characteristics, such as the development of elastic instabilities or the transition from laminar to turbulent flow.

