Euler Number
Euler number is proportional to { (friction head) * (velocity head) } and is used in momentum transfer in general and fluid friction in conduits calculations in particular. It is equivalent to (N/2) where N is the number of velocity heads.
It is normally defined in one of the following forms :
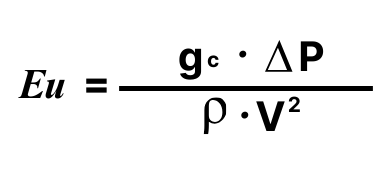
or
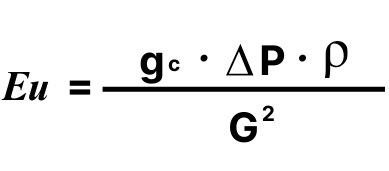
Where: | ||
delta-P | = | Pressure drop |
gc | = | Dimensional constant |
G | = | Mass velocity |
rho | = | Density |
V | = | Velocity |
The Euler number is often used in the analysis of fluid flows to determine whether inertial effects dominate over pressure effects or vice versa. For example, high Euler numbers indicate that inertial forces are dominant, suggesting the flow is fast and turbulent, while low Euler numbers suggest that pressure forces are dominant, indicating slower, more laminar flow.

